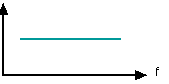BASS TIP-UP IN RIBBON MICS
THE "PROXIMITY EFFECT"
PLAN VIEW OF A RIBBON MIC
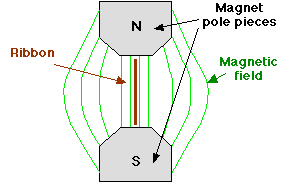
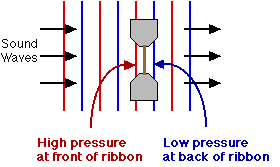
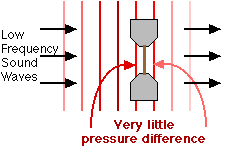
The ribbon is vibrated across the magnetic field by differences in air pressure between the two sides caused by a sound wave.
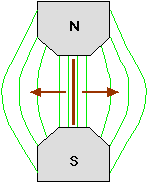
The output voltage of the ribbon is proportional to the velocity with which is moves across the magnetic field and this depend on the pressure difference and the frequency.
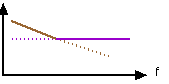
Because of the mass of the ribbon, with a constant pressure difference, the output voltage falls as the frequency gets higher
GRAPH OF OUTPUT VOLTAGE AGAINST FREQUENCY

The pressure difference is caused by sound waves, alternate waves of increased and decreased air pressure.
The sound waves can be plane waves or spherical waves or, more usually, a mixture of the two.
|
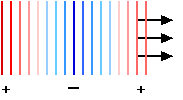
FROM A DISTANCE OR FROM A FLAT SOURCE
Alternate waves of constant strength. Normally this effect is strongest
|
|
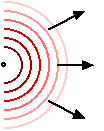
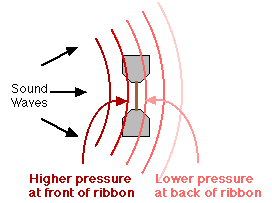
CLOSE TO A POINT SOURCE
Each wave expands and weakens. Normally this is a much smaller effect unless you are close to the source
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
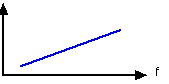
The closer to the sound source, the stronger this effect becomes.
|
|
|
|
|
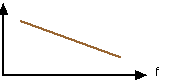
With this information we can see how ribbon microphone responds to the two different types of wave and what happens in the practical situation when it is brought close to a source of sound and spherical waves begin to dominate the response.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WITH BOTH PLANE AND SPHERICAL WAVES
|
||